Product Description
|
Hello There, All the parts we made are customized, so you are checking what we have done for other brands/customers. You might have similar parts needs to be done, or something very different from theirs. It’s all good. If you need anything made using CNC turning, milling or Sheetmetal process, our team are here to help. Please don’t worry about the safety of your drawings, we will use them only for you, and won’t post the parts images without your approval. |
Below Are Some Details You Need To Know:
– The drawing/idea we need from you:
—If you have design/drawings, we will prefer DWG, STEP, IGES, DXF, and also PDF file (if there are critical dimensions);
—If you don’t have drawing, you can send us solid sample, and we will make parts for you as per the sample;
—If you have ideas only, you can send hand draft and with some details description, our engineers could draw for you;
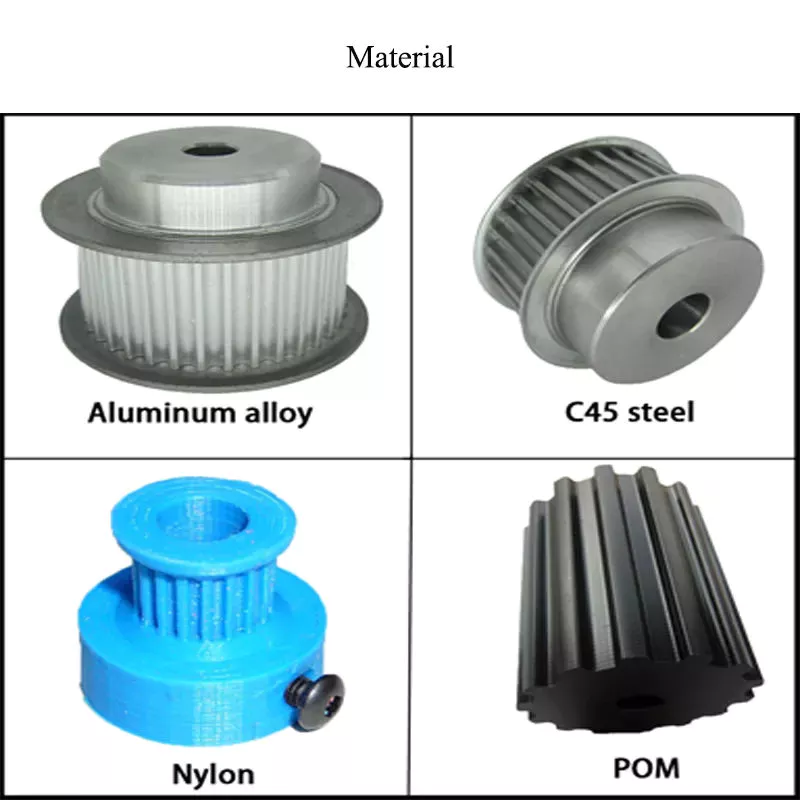
– Materials to choose from:
~Aluminum,
~Titanium,
~Stainless steel,
~Brass,
~Copper,
~Plastics (Delrin, PEEK, HDPE, PTFE, ABS, PVC),
– Surface Treatment:
~Anodization,
~Hard coat anodization,
~Plating,
~Passivation,
~Beadblasting,
~Polish,
~Brush,
~Tumbling (also called intense vibro deburring)
—-These material and surface are most commonly used, if you need other specific material and surface, please feel free to ask, chances we are CZPT to exceed your expectation.
– Lead Time:
For sample orders, usually take around 2 week or less. For production around 3-4 weeks. (But it varies with different complexity of the work);
– Shipping Methods:
~Courier service: DHL, FedEx, UPS, TNT
~Air Freight for parts over 100kgs will be much more cost effective;
~Ocean freight for orders that is heavy and need a lot of space;
– Machines & Team Images
“It’s not what we do, it’s how we do it”
If you need premium quality parts, we are the 1 for you.
| It’s simple to work with us, here are some steps:
*Step 1: Send us inquiry with all the information you have for the parts you want to make (including drawings, special request, Tolerance etc) ; *Step 2: GBD will send you quote/ review the file for you, and then give you quotation or proposal if there is any; *Step 3: Customers agree the price and send prepayment, or make changes in order to get the costs down; *Step 4: GBD Prepare all the paperwork, purchase the material and get the parts machined, (There might be technical details communication if needed, in order to make the parts come out as good as you expected). Doing quality inspection, and send updates of the parts for customers; *Step 5: GBD Pack the parts and get the parts ready to ship, and send tracking information for customers; *Step 6: GBD keep tracking the status of the package until package is delivered, and get feedback from customers; *Step 7: If there is any quality issue with the parts, GBD will take good care of it. |
As you can see, you just need to name your demand, and GBD Team will roll up the sleeves and get the job done. 🙂
We can’t wait to hear from you!
-GBD Machining Team
How to use the pulley system
Using a pulley system is a great way to move things around your home, but how do you use a pulley system? Let’s look at the basic equations that describe a pulley system, the types of pulleys, and some safety considerations when using pulleys. Here are some examples. Don’t worry, you’ll find all the information you need in 1 place!
Basic equations of pulley systems
The pulley system consists of pulleys and chords. When the weight of the load is pulled through the rope, it slides through the groove and ends up on the other side. When the weight moves, the applied force must travel nx distance. The distance is in meters. If there are 4 pulleys, the distance the rope will travel will be 2×24. If there are n pulleys, the distance traveled by the weight will be 2n – 1.
The mechanical advantage of the pulley system increases with distance. The greater the distance over which the force is applied, the greater the leverage of the system. For example, if a set of pulleys is used to lift the load, 1 should be attached to the load and the other to the stand. The load itself does not move. Therefore, the distance between the blocks must be shortened, and the length of the line circulating between the pulleys must be shortened.
Another way to think about the acceleration of a pulley system is to think of ropes and ropes as massless and frictionless. Assuming the rope and pulley are massless, they should have the same magnitude and direction of motion. However, in this case the quality of the string is a variable that is not overdone. Therefore, the tension vector on the block is labeled with the same variable name as the pulley.
The calculation of the pulley system is relatively simple. Five mechanical advantages of the pulley system can be found. This is because the number of ropes supporting the load is equal to the force exerted on the ropes. When the ropes all move in the same direction, they have 2 mechanical advantages. Alternatively, you can use a combination of movable and fixed pulleys to reduce the force.
When calculating forces in a pulley system, you can use Newton’s laws of motion. Newton’s second law deals with acceleration and force. The fourth law tells us that tension and gravity are in equilibrium. This is useful if you need to lift heavy objects. The laws of motion help with calculations and can help you better understand pulley systems.
Types of pulleys
Different types of pulleys are commonly used for various purposes, including lifting. Some pulleys are flexible, which means they can move freely around a central axis and can change the direction of force. Some are fixed, such as hinges, and are usually used for heavier loads. Others are movable, such as coiled ropes. Whatever the purpose, pulleys are very useful in raising and lowering objects.
Pulleys are common in many different applications, from elevators and cargo lift systems to lights and curtains. They are also used in sewing machine motors and sliding doors. Garage and patio doors are often equipped with pulleys. Rock climbers use a pulley system to climb rocks safely. These pulley systems have different types of pinions that allow them to balance weight and force direction.
The most common type of pulley is the pulley pulley system. The pulley system utilizes mechanical advantages to lift weight. Archimedes is thought to have discovered the pulley around 250 BC. in ancient Sicily. Mesopotamians also used pulleys, they used ropes to lift water and windmills. Pulley systems can even be found at Stonehenge.
Another type of pulley is called a compound pulley. It consists of a set of parallel pulleys that increase the force required to move large objects. This type is most commonly used in rock climbing and sailing, while composite pulleys can also be found in theater curtains. If you’re wondering the difference between these 2 types of pulleys, here’s a quick overview:
Mechanical Advantages of Pulley Systems
Pulley systems offer significant mechanical advantages. The ability of the system to reduce the effort required to lift weights increases with the number of rope loops. This advantage is proportional to the number of loops in the system. If the rope had only 1 loop, then a single weight would require the same amount of force to pull. But by adding extra cycles, the force required will be reduced.
The pulley system has the advantage of changing the direction of the force. This makes it easier to move heavy objects. They come in both fixed and mobile. Pulleys are used in many engineering applications because they can be combined with other mechanisms. If you want to know what a pulley can do, read on! Here are some examples. Therefore, you will understand how they are used in engineering.
Single-acting pulleys do not change direction, but compound pulleys do. Their mechanical advantage is six. The compound pulley system consists of a movable pulley and a fixed pulley. The mechanical advantage of the pulley system increases as the number of movable wheels decreases. So if you have 2 wheels, you need twice as much force to lift the same weight because you need a movable pulley.
The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be maximized by adding more pulleys or rope lengths. For example, if you have a single pulley system, the mechanical advantage is 1 of the smallest. By using 2 or 3 pulleys, up to 5 times the mechanical advantage can be achieved. You can also gain up to 10 times the mechanical advantage by using multiple pulley systems.
The use of a single movable pulley system also adds to the mechanical advantage of the pulley system. In this case, you don’t have to change the direction of the force to lift the weight. In contrast, a movable pulley system requires you to move the rope farther to generate the same force. Using a compound pulley system allows you to lift heavy loads with ease.
Safety Issues When Using Pulley Systems
Pulleys have an incredibly unique structure, consisting of a disc with a groove in the middle and a shaft running through it. A rope or cord is attached to 1 end of a pulley that turns when force is applied. The other end of the rope is attached to the load. This mechanical advantage means that it is much easier to pull an object using the pulley system than to lift the same object by hand.
Although pulley systems are a common part of many manufacturing processes, some employers do not train their workers to use them properly or install protection to prevent injury. It is important to wear proper PPE and follow standard laboratory safety practices during pulley system activities. Make sure any support structures are strong enough to handle the weight and weight of the rope or rope. If you do fall, be sure to contact your employer immediately.